30-04-2021
Splunk Search Commands Cheat Sheet
When I first started learning about the Splunk search commands, I found it challenging to understand the benefits of each command, especially how the BY clause impacts the output of a search. It wasn't until I did a comparison of the output (with some trial and a whole lotta error) that I was able to understand the differences between the commands.
- Splunk uses the rex command to perform Search-Time substitutions. Rex Command Use Rex to Perform SED Style Substitutions Set the mode s for substitute g for global.
- Search for events around events associated with 'root' and 'login', and then search login root localize maxspan=5m maxpause=5m map search= each of those time ranges for 'failure'. 'search failure starttimeu=$starttime$ endtimeu=$endtime$' Create a search string from the values of the host, source and sourcetype fields.
- The lookup command adds fields based on looking at the value in an event, referencing a lookup table, and adding the fields in matching rows in the lookup table to your event. These commands can be used to create new fields or they can be used to overwrite the values of existing fields. The fields command removes fields from search results.
The search commands that make up the Splunk Light search processing language are a subset of the Splunk Enterprise search commands. The table below lists all of the commands that make up the Splunk Light search processing language sorted alphabetically
This topic links to the Splunk Enterprise Search Reference for each search command.
| Command | Description | See also |
|---|---|---|
abstract | Produces a summary of each search result. | highlight |
accum | Keeps a running total of the specified numeric field. | autoregress, delta, trendline, streamstats |
addcoltotals | Computes an event that contains sum of all numeric fields for previous events. | addtotals, stats |
addinfo | Add fields that contain common information about the current search. | search |
addtotals | Computes the sum of all numeric fields for each result. | addcoltotals, stats |
analyzefields | Analyze numerical fields for their ability to predict another discrete field. | anomalousvalue |
anomalies | Computes an 'unexpectedness' score for an event. | anomalousvalue, cluster, kmeans, outlier |
anomalousvalue | Finds and summarizes irregular, or uncommon, search results. | analyzefields, anomalies, cluster, kmeans, outlier |
append | Appends subsearch results to current results. | appendcols, appendcsv, join, set |
appendcols | Appends the fields of the subsearch results to current results, first results to first result, second to second, etc. | append, appendcsv, join, set |
appendpipe | Appends the result of the subpipeline applied to the current result set to results. | append, appendcols, join, set |
arules | Finds association rules between field values. | associate, correlate |
associate | Identifies correlations between fields. | correlate, contingency |
audit | Returns audit trail information that is stored in the local audit index. | |
autoregress | Sets up data for calculating the moving average. | accum, autoregress, delta, trendline, streamstats |
bin, discretize | Puts continuous numerical values into discrete sets. | chart, timechart |
bucketdir | Replaces a field value with higher-level grouping, such as replacing filenames with directories. | cluster, dedup |
chart | Returns results in a tabular output for charting. See Functions for stats, chart, and timechart in the Splunk Enterprise Search Reference. | timechart |
cluster | Clusters similar events together. | anomalies, anomalousvalue, cluster, kmeans, outlier |
concurrency | Uses a duration field to find the number of 'concurrent' events for each event. | timechart |
contingency, counttable, ctable | Builds a contingency table for two fields. | associate, correlate |
convert | Converts field values into numerical values. | eval |
correlate | Calculates the correlation between different fields. | associate, contingency |
dbinspect | Returns information about the specified index. | |
dedup | Removes subsequent results that match a specified criteria. | uniq |
delta | Computes the difference in field value between nearby results. | accum, autoregress, trendline, streamstats |
diff | Returns the difference between two search results. | |
erex | Allows you to specify example or counter example values to automatically extract fields that have similar values. | extract, kvform, multikv, regex, rex, xmlkv |
eval | Calculates an expression and puts the value into a field. See Functions for eval and where in the Splunk Enterprise Search Reference. | where |
eventcount | Returns the number of events in an index. | dbinspect |
eventstats | Adds summary statistics to all search results. | stats |
extract, kv | Extracts field-value pairs from search results. | kvform, multikv, xmlkv, rex |
fieldformat | Expresses how to render a field at output time without changing the underlying value. | eval, where |
fields | Removes fields from search results. | |
fieldsummary | Generates summary information for all or a subset of the fields. | af, anomalies, anomalousvalue, stats |
filldown | Replaces NULL values with the last non-NULL value. | fillnull |
fillnull | Replaces null values with a specified value. | |
findtypes | Generates a list of suggested event types. | typer |
foreach | Run a templatized streaming subsearch for each field in a wildcarded field list. | eval |
format | Takes the results of a subsearch and formats them into a single result. | |
from | Retrieves data from a dataset, such as a data model dataset, a CSV lookup, a KV Store lookup, a saved search, or a table dataset. | |
gauge | Transforms results into a format suitable for display by the Gauge chart types. | |
gentimes | Generates time-range results. | |
geostats | Generate statistics which are clustered into geographical bins to be rendered on a world map. | stats, xyseries |
head | Returns the first number n of specified results. | reverse, tail |
highlight | Causes Splunk Web to highlight specified terms. | |
history | Returns a history of searches formatted as an events list or as a table. | search |
input | Adds sources to Splunk or disables sources from being processed by Splunk. | |
inputcsv | Loads search results from the specified CSV file. | loadjob, outputcsv |
iplocation | Extracts location information from IP addresses. | |
join | SQL-like joining of results from the main results pipeline with the results from the subpipeline. | selfjoin, appendcols |
kmeans | Performs k-means clustering on selected fields. | anomalies, anomalousvalue, cluster, outlier |
kvform | Extracts values from search results, using a form template. | extract, kvform, multikv, xmlkv, rex |
loadjob | Loads events or results of a previously completed search job. | inputcsv |
localize | Returns a list of the time ranges in which the search results were found. | map, transaction |
makecontinuous | Makes a field that is supposed to be the x-axis continuous (invoked by chart/timechart) | chart, timechart |
makemv | Change a specified field into a multivalued field during a search. | mvcombine, mvexpand, nomv |
map | A looping operator, performs a search over each search result. | |
mcollect | Converts search results into metric data and inserts the data into a metric index on the search head. | collect, meventcollect |
metadata | Returns a list of source, sourcetypes, or hosts from a specified index or distributed search peer. | dbinspect |
metasearch | Retrieves event metadata from indexes based on terms in the logical expression. | metadata, search |
meventcollect | Converts search results into metric data and inserts the data into a metric index on the indexers. | collect, mcollect |
mstats | Calculates statistics for the measurement, metric_name, and dimension fields in metric indexes. | stats |
multikv | Extracts field-values from table-formatted events. | |
multisearch | Run multiple streaming searches at the same time. | append, join |
mvcombine | Combines events in search results that have a single differing field value into one result with a multivalue field of the differing field. | mvexpand, makemv, nomv |
mvexpand | Expands the values of a multivalue field into separate events for each value of the multivalue field. | mvcombine, makemv, nomv |
nomv | Changes a specified multivalued field into a single-value field at search time. | makemv, mvcombine, mvexpand |
outlier | Removes outlying numerical values. | anomalies, anomalousvalue, cluster, kmeans |
outputcsv | Outputs search results to a specified CSV file. | inputcsv, outputtext |
outputtext | Ouputs the raw text field (_raw) of results into the _xml field. | outputtext |
predict | Enables you to use time series algorithms to predict future values of fields. | x11 |
rangemap | Sets RANGE field to the name of the ranges that match. | |
rare | Displays the least common values of a field. | stats, top |
regex | Removes results that do not match the specified regular expression. | rex, search |
relevancy | Calculates how well the event matches the query. | |
reltime | Converts the difference between 'now' and '_time' to a human-readable value and adds adds this value to the field, 'reltime', in your search results. | convert |
rename | Renames a specified field; wildcards can be used to specify multiple fields. | |
replace | Replaces values of specified fields with a specified new value. | |
rest | Access a REST endpoint and display the returned entities as search results. | |
return | Specify the values to return from a subsearch. | format, search |
reverse | Reverses the order of the results. | head, sort, tail |
rex | Specify a Perl regular expression named groups to extract fields while you search. | extract, kvform, multikv, xmlkv, regex |
rtorder | Buffers events from real-time search to emit them in ascending time order when possible. | |
savedsearch | Returns the search results of a saved search. | |
script, run | Runs an external Perl or Python script as part of your search. | |
scrub | Anonymizes the search results. | |
search | Searches Splunk indexes for matching events. | |
searchtxn | Finds transaction events within specified search constraints. | transaction |
selfjoin | Joins results with itself. | join |
sendemail | Emails search results to a specified email address. | |
set | Performs set operations (union, diff, intersect) on subsearches. | append, appendcols, join, diff |
setfields | Sets the field values for all results to a common value. | eval, fillnull, rename |
sort | Sorts search results by the specified fields. | reverse |
spath | Provides a straightforward means for extracting fields from structured data formats, XML and JSON. | xpath |
stats | Provides statistics, grouped optionally by fields. See Functions for stats, chart, and timechart in the Splunk Enterprise Search Reference. | eventstats, top, rare |
strcat | Concatenates string values. | |
streamstats | Adds summary statistics to all search results in a streaming manner. | eventstats, stats |
table | Creates a table using the specified fields. | fields |
tags | Annotates specified fields in your search results with tags. | eval |
tail | Returns the last number n of specified results. | head, reverse |
timechart | Create a time series chart and corresponding table of statistics. See Functions for stats, chart, and timechart in the Splunk Enterprise Search Reference. | chart, bucket |
top | Displays the most common values of a field. | rare, stats |
transaction | Groups search results into transactions. | |
transpose | Reformats rows of search results as columns. | |
trendline | Computes moving averages of fields. | timechart |
typeahead | Returns typeahead information on a specified prefix. | |
typer | Calculates the eventtypes for the search results. | typelearner |
uniq | Removes any search that is an exact duplicate with a previous result. | dedup |
untable | Converts results from a tabular format to a format similar to stats output. Inverse of xyseries and maketable. | |
where | Performs arbitrary filtering on your data. See Functions for eval and where in the Splunk Enterprise Search Reference. | eval |
x11 | Enables you to determine the trend in your data by removing the seasonal pattern. | predict |
xmlkv | Extracts XML key-value pairs. | extract, kvform, multikv, rex |
xmlunescape | Unescapes XML. | |
xpath | Redefines the XML path. | |
xyseries | Converts results into a format suitable for graphing. |
< Back |Home| Next >
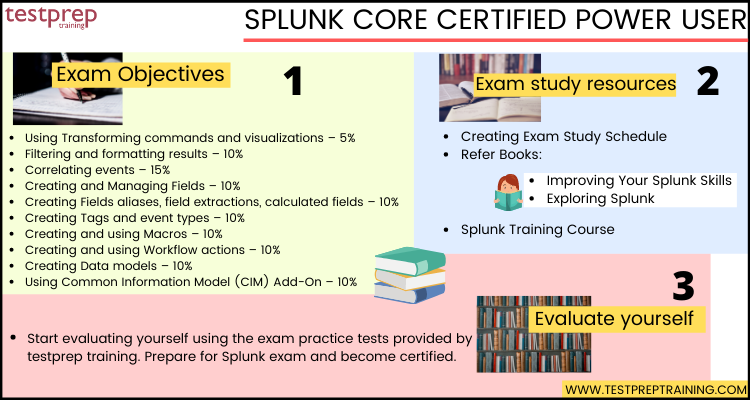
Splunk Search Commands Cheat Sheet Printable
- Most frequently used splunk commands.
1. check splunk status or check if splunk is running in linux
./splunk status
2. start splunk
/.splunk start
3. stop splunk
./splunk stop
4. start splunk in debug mode
./splunk start --debug
5. check on what port splunk is running or listening
netstat -an | grep splunk
6.check cpu usage by splunk
top
7. What splunk thinks of configurations (Using Btool)
./splunk cmd btool list
./splunk cmd btool list --debug
./splunk cmd btool web list --debug
--debug tells where it is reading the configuration from
8. Deployment Server commands
./splunk list deploy-clients
./splunk reload
./splunk reload deploy-server -class <ServerClass>
9.monitor files in a directory i.e. add logs to splunk from a directory
./splunk add monitor /path to log file
Splunk Quick Reference Guide Pdf

< Back |Home| Next >
